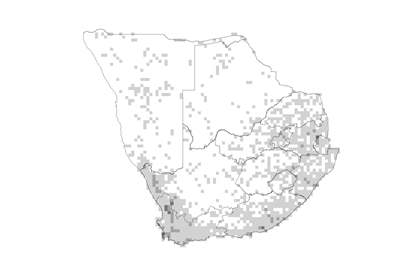
 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
(excluding Agapanthaceae and Alliaceae)Clivia family
The family Amaryllidaceae consists of bulbous plants which are widely cultivated for horticultural purposes. The leaves are frequently distichous and strap-shaped to linear. The inflorescences are scapose (borne on a leafless stalk) with the flowers arranged in an umbel-like cluster.
Distribution
Found mainly in warm temperate and tropical regions. The centres of diversity are South America, southern Africa and the Mediterranean. In southern Africa the highest diversity is in the Western Cape and along the West Coast through Namaqualand to southern Namibia.
Number of genera in the world
ca. 60
Number of species in the world
ca. 800
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
20
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
266
Well-known southern African genera
Ammocharis, Boophone, Brunsvigia, Clivia, Crinum, Cyrtanthus, Gethyllis, Haemanthus, Nerine, Scadoxus
Growth forms
Herbaceous, perennial or biennial, bulbous or rarely rhizomatous (Scadoxus).
Habitats
Grassland, savanna and wetlands. Many taxa are adapted to dry habitats.
Flagship species
Crinum macowanii (river lily; rivierlelie [A]; umnduze [Z]) grows almost up to 1 m tall, has lovely large, trumpet-shaped, white and pink-striped flowers which are pleasantly scented. This plant is used as a traditional medicine for treating urinary infections and the relief of itchy rashes. Various parts are used as bandages and according to folklore even as protective charms. In gardens it can be used with success as a focus plant and even when not flowering the leaves are quite attractive. (Photo: GN).
Significance of the family
The family is renowned for its use in horticulture. Many species are large-flowered and are cultivated for the cut flower industry. Some genera have a potential for medicinal use due to their anticancer properties. The mashed bulbs or fibrous tunic layers are used as dressings to heal wounds and for skin and digestive disorders. The fruits of Gethyllis, commonly known as kukumakranka, are used as flavourants and perfumes. The bulbs of many amaryllids are toxic to pets like cats and dogs; symptoms of poisoning may include vomiting, salivation and diarrhoea.
Diagnostic characters
Mostly geophytes with bulbs. Leaves narrowly to broadly strap-shaped, or elliptical, mostly in 2 rows , usually glabrous. Inflorescence an umbel-like cluster at the end of a leafless stalk (scape) . Flowers regular , mostly supported by 2 or rarely up to 8 bracts . Perianth in 2 whorls of 3 tepals each, usually showy . Anthers 6, in 2 whorls of 3 each. Ovary inferior, sometimes visible as thickening at base of a long tube, 3-locular. Fruit a capsule (with dry or fleshy seeds) or a fleshy berry .
Did you know?
Clivia is a widely cultivated genus and some cultivars fetch the highest prices for any amaryllid in the world.