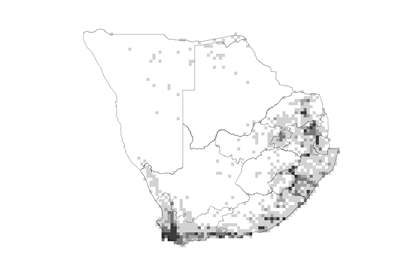
 Species distribution and density. Darker squares represent higher density of members of this family. |
Introduction
Orchid family
A family with highly specialised flowers, adapted for insect pollination. Fruits contain thousands of seeds that are so small that they appear dust-like when dispersed by the wind. The family is cosmopolitan and has many uses apart from their attractive, colourful flowers used in the flower industry.
Distribution
Cosmopolitan, distributed from the tropics to the subarctic zone. Infrequently found in dry areas or high altitudes. Southern Africa has high levels of diversity in the Western Cape and along the Drakensberg escarpment.
Number of genera in the world
ca. 800
Number of species in the world
ca. 20 000
Number of genera in the Flora of southern Africa region
53
Number of species in the Flora of southern Africa region
529
Well-known southern African genera
Bonatea, Brownleea, Corycium, Disa, Eulophia, Habenaria, Holothrix, Mystacidium, Polystachya, Satyrium
Growth forms
Terrestrial, epilithic or epiphytic, very rarely a climber (e.g. Vanilla). Mostly deciduous perennial herbs, with rhizomes, corms, tuberous roots or pseudobulbs.
Habitats
Bushveld, savanna, karroid and thorn scrub, fynbos and grassland; often associated with wetlands.
Flagship species
Disa uniflora (red disa; rooidisa [A]) grows along stream banks and in moist places and makes a spectacular display when in full bloom during the summer months. This species is one of the best known South African orchids and the floral emblem of the Western Cape. The red disa has been grown in England at least since 1891 and is the parent to many hybrids cultivated by orchid growers. The flowers are usually red but can vary from pink to yellow and even white. It is also cultivated in New Zealand as a cut flower. (Photo: RO).
Significance of the family
The main economic importance of the family is in the flower industry as ornamentals and long-lasting cut flowers. The Mexican species *Vanilla planiflora has long been cultivated for the aromatic flavour of its pods (beans). The tubers of some African species (e.g. Satyrium) are harvested as a food source. A large number of species are used in traditional medicines. Various parts of orchids are used in traditional folklore in Africa as love, death and fertility charms, to ward off evil or as protection from lightning. Some species are also used as aphrodisiacs. (Photo: RDV).
Diagnostic characters
Herbs usually with rhizomes, pseudobulbs or tubers . Leaves alternate, usually basal, spirally arranged or in 2 rows with parallel veins. Flowers irregular with complex structure . Androecium and gynoecium fused into a gynandrium �. Calyx consists of 3 sepals, green or coloured. Corolla consists of 3 petals, lower one modified into a lip . Stamens not visible and highly modified and fused with style to form a column. Pollen aggregated into a waxy clump to form pollinia, sometimes covered by anther caps �. Ovary inferior �, 1-locular with 3 carpels. Fruit a capsule with numerous minute seeds.
Did you know?
The Orchidaceae is one of the largest flowering plant families and, in addition to the natural species, more than 70 000 cultivars and hybrids have been cultivated from this family.