Click on images to enlarge

habit (Photo: Sheldon Navie)

habit (Photo: Sheldon Navie)

stems and lower leaves borne on long stalks (Photo: Sheldon Navie)

upper leaves (Photo: Sheldon Navie)

close-up of upper leaves and male flower clusters (Photo: Sheldon Navie)

ribbed stems, female flowers and immature fruit (Photo: Sheldon Navie)

close-up of leaf underside and immature fruit (Photo: Sheldon Navie)
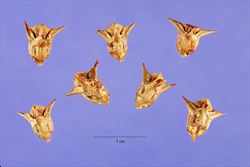
close-up of mature fruit (Photo: Steve Hurst at USDA PLANTS Database)
Scientific Name
Emex australis Steinh.
Synonyms
Emex centropodium Meisn.
Family
Polygonaceae
Common Names
bull head, bullhead, Cape spinach, cat's head, catsheads, devil's face, devil's thorn, double gee, doublegee, giant bull head, goat head, goathead, goat's head burr, jackie, prickly jack, southern three-corner jack, southern threecornerjack, spiny emex, three corner jack, three cornered jack, three-corner jack, three-cornered jack
Origin
Native to southern Africa (i.e. Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland).
Naturalised Distribution
A very widely naturalised species that is particularly common in the sub-coastal districts of temperate Australia. It is most abundant in the western and southern parts of Western Australia and is also common in parts of New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia and south-eastern Queensland. Also present in other parts of Queensland, in the southern parts of the Northern Territory and in Tasmania (i.e. on Flinders Island).
It is also regarded as a weed in the USA, Taiwan and New Zealand.
Notes
This species is sometimes regarded as an environmental weed in Victoria and Western Australia and was recently listed as a priority environmental weed in one Natural Resource Management region. Spiny emex (Emex australis) is a common weed of agricultural areas, particularly crops, and disturbed habitats (e.g. roadsides, tracks, firebreaks, picnic sites, old homesteads and clearings). However, it is often present in highly disturbed sites in conservation reserves and also invades natural areas including creekbanks, river floodplains, claypans, the edges of saline lakes and granite rock areas.
In Western Australia, it invades naturally disturbed and high productivity areas in arid and semi-arid regions. It is also common in conservation areas in these regions, which are important sites of biological diversity. For example, it has been recorded from Rudall River, Cape Range, Mount Augustus, Kennedy Range, Zuytdorp, Francois Peron, Goongarrie and Boorabbin National Parks. It is also a major weed on floodplains along the Murchison River in Kalbarri National Park and is regarded as a high priority environmental weed in conservation reserves in the Shark Bay region (e.g. in the lower Yardie Creek Gorge). Spiny emex (Emex australis) is also a major weed of naturally disturbed and nutrient enriched seabird rookeries of the Abrolhos Islands near Geraldton.
In Victoria, spiny emex (Emex australis) is regarded as a serious threat to lowland grassland and grassy woodlands (e.g. in Goulburn Broken Catchment). It also occurs along roadsides and firebreaks in conservation areas in semi-arid western New South Wales (e.g. in Willandra and Cocoparra National Parks) and is listed as an ephemeral weed which may have a significant impact on native vegetation in Kinchega National Park in south-western New South Wales. In South Australia it is present in a variety of habitats (e.g. semi-arid vegetation, coastal dunes, offshore islands and along roadsides) within conservation areas (e.g. Aldinga Scrub Conservation Park, Coorong National Park, Flinders Ranges National Park and Black Hill Conservation Park). It has also been recorded in conservation areas in south-western Queensland (e.g. Currawinya National Park) and the Northern Territory (e.g. Wattarka National Park and Uluru National Park).

